In WordPress, user permissions determine the actions each user role is allowed to perform on your site. By default, there are five user roles available, and you can assign one to each user based on their responsibilities.
This allows certain users to have complete control over your website, while others may only be able to view content. Most users will fall somewhere in between these two extremes.
As your WordPress site expands, understanding user roles and permissions becomes essential.
What Are User Permissions in WordPress?
User permissions provide you with full control over your WordPress site by restricting the access levels of other users. It’s essential to grant users only the capabilities necessary for their specific roles, as this practice can significantly enhance your website’s security.
Consider that a WordPress site requires various tasks to operate efficiently, referred to as ‘capabilities’, of which there are more than 70 available. Here are a few examples:
- Installing WordPress plugins
- Adding new blog posts
- Editing other users’ blog posts
- Publishing and scheduling content
- Moderating comments and deleting spam
- Deleting or unpublishing content
- Adding new users
It’s important to restrict full access to your website for every user, as not all tasks should be performed by all individuals.
For instance, allowing a guest blogger to install plugins or delete content would be unwise. Fortunately, WordPress includes a user role management system that enables you to assign permissions tailored to specific roles, allowing users to perform only the functions necessary for their responsibilities.
To enhance the security of your WordPress site, make sure to assign users a role that matches their needs without granting excessive capabilities. Let’s explore the various user roles available in WordPress.
WordPress User Roles and Permissions
In WordPress, a user is an individual who has registered on your site, allowing them to log in using a username and password.
Each user is assigned a specific role that dictates their capabilities on the website. On a standard WordPress site, there are five default user roles, with a sixth role available in a multisite setup. Let’s briefly examine each of these roles:
- Subscribers: can log into the site, edit their profiles, and view published content, but that’s where their access ends.
- Contributors: are allowed to add new posts and edit their own submissions, but they cannot publish, delete posts, or upload files.
- Authors: can write, edit, publish, and delete their own posts; however, they cannot modify posts created by others. They can upload files and view comments, but do not have permission to moderate them.
- Editors: have the ability to write, edit, publish, and delete posts from themselves and others. They can also upload files, create new categories, and moderate comments.
- Administrators: possess full control over the website and are the only role capable of changing site settings, installing themes and plugins, adding users, and performing other administrative functions.
- Super Administrators: have admin access across all sites within a WordPress multisite network.
Here’s a bulleted list summarizing the roles and their permissions:
You can customize the permissions for each role and even create new ones tailored to your site’s requirements. For the sake of security, it’s advisable to assign users the minimum permissions necessary for their roles, particularly steering clear of granting admin access. Strive to keep the number of admin users to a minimum.
How to Assign a Role to a User
As an administrator of your website, you have the ability to effortlessly add new users and assign them specific roles.
As an administrator of your website, you can easily add new users and assign them specific roles. To begin, navigate to User » Add New in your WordPress dashboard.
Next, fill in the required information for the new user. When you get to the ‘Role’ section, simply select the appropriate role for the user from the drop-down menu.
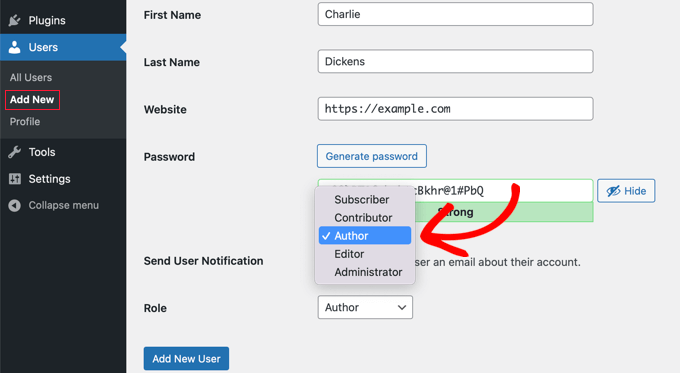
After completing this step, the new WordPress user can log in and will have access to the permissions associated with their specific role.
You can modify their role at any time by going to Users » All Users and selecting a different role in their user profile. For further information, please refer to our guide on adding new users to your WordPress blog.
How to Customize WordPress User Roles and Permissions
The default user roles in WordPress come with capabilities suitable for the majority of websites and blogs.
For instance, if you manage a magazine site, you can assign the Editor role to senior staff members, the Author role to junior staff, and the Contributor role to guest writers.
However, there may be occasions when you want to tailor the permissions and capabilities of these roles to better fit your website’s specific requirements. Additionally, you have the option to create new user roles with customized sets of permissions.
There might also be instances when you wish to enhance a user role’s permissions; for example, allowing Contributors to edit their posts after they have been approved.
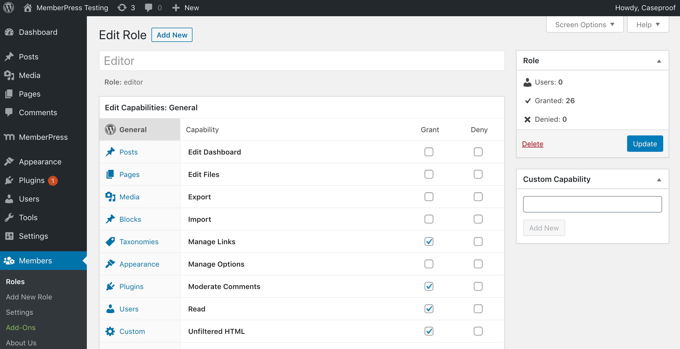
Alternatively, you might consider limiting certain capabilities of a role. For instance, you could confine authors to a specific category or stop them from deleting posts.
To learn how to modify existing user roles and create new ones, check out our guide on adding or removing capabilities for user roles in WordPress.
We hope this article has helped you better understand user permissions in WordPress.
Additionally, take a look at our Additional Reading list below for related articles with useful WordPress tips, tricks, and ideas. If you enjoyed this article, please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials, and connect with us on Twitter and Facebook.


